This post may contain affiliate links which means I may receive a commission for purchases made through links. Learn more on my Private Policy page.
Are you a beginner looking to understand irrigation system components? Look no further! This article is here to guide you through the basics of irrigation system components, giving you a clear understanding of the essential parts that make up a well-designed system. From sprinklers to controllers, we’ll break down each component and explain its role in ensuring your plants receive the right amount of water at the right time. Whether you’re a homeowner or a budding gardener, this guide will equip you with the knowledge needed to create a thriving and efficient irrigation system. So let’s get started and demystify the world of irrigation system components!
Introduction to Irrigation Systems
What is an irrigation system?
An irrigation system is a network of components and devices designed to provide water to plants in a controlled and efficient manner. It helps deliver the necessary amount of water at the right time and in the right place to promote healthy plant growth.
Why is it important?
Irrigation systems are crucial for sustaining agricultural production and maintaining landscapes, particularly in areas where water resources are limited or unreliable. These systems ensure that plants receive adequate water, reducing water waste and enabling efficient water management.
Types of irrigation systems
There are several types of irrigation systems available, each with its own advantages and suitable applications. The main types include:
-
Flood or Surface Irrigation: This method involves flooding the field or garden with water, allowing it to evenly distribute and infiltrate the soil. It is commonly used for large agricultural areas with level terrain.
-
Sprinkler Irrigation: Sprinkler systems use overhead sprinklers or spray heads to deliver water in the form of rain-like droplets. It is suitable for various crops, orchards, and gardens.
-
Drip Irrigation: Drip systems deliver water directly to the plant’s root zone through a network of tubes and emitters. It is highly efficient and minimizes water loss due to evaporation and runoff. Drip irrigation is commonly used in gardens and for certain agricultural crops.

Water Source
Types of water sources
The water source for an irrigation system can vary depending on the location and availability of water resources. Common water sources include:
-
Municipal Water Supply: Many irrigation systems connect to the municipal water supply, which provides a reliable source of water. However, it is essential to consider the water quality, potential for restrictions, and associated costs.
-
Surface Water: Rivers, lakes, and ponds can serve as water sources for irrigation. However, careful consideration must be given to water rights, permits, and potential environmental impacts.
-
Groundwater: Wells and underground aquifers can provide a consistent water source. However, it is crucial to monitor groundwater levels to prevent overextraction and protect the environment.
Importance of choosing the right water source
Selecting the appropriate water source for your irrigation system is vital to ensure the health and productivity of your plants. Factors to consider include water quality, availability, sustainability, and legal considerations. Adequate planning and careful decision-making can help optimize the irrigation system’s efficiency and longevity.

Water Delivery Methods
Surface irrigation
Surface irrigation involves flooding the field or garden with water. It relies on gravity to distribute water across the land, allowing it to infiltrate the soil and reach the plant roots. This method is suitable for level terrains and crops that can tolerate wet conditions.
Sprinkler irrigation
Sprinkler irrigation utilizes overhead sprinklers or spray heads to deliver water in a manner similar to rainfall. The water is distributed in a circular pattern, covering a specific area. This method is flexible and can be adapted to various crops, including those with canopy cover.
Drip irrigation
Drip irrigation is a highly efficient method that delivers water directly to the plant’s root zone. It involves a network of tubes and emitters that release water in controlled amounts. Drip irrigation reduces water waste, minimizes evaporation and runoff, and is suitable for various crops, gardens, and landscapes.

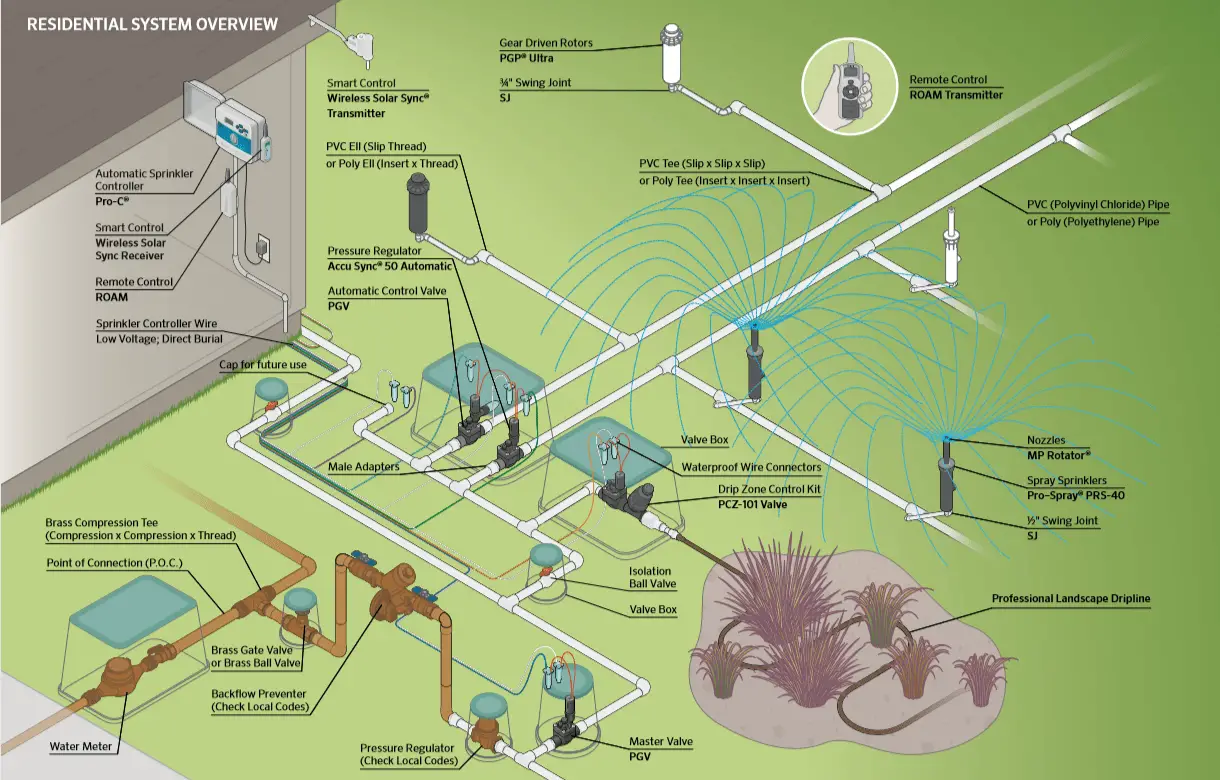
Main Components of an Irrigation System
Control system
The control system is the brain of an irrigation system. It allows you to set and adjust the watering schedule, monitor water usage, and control other system components. The main components of a control system include:
Controller
The controller is the central unit that connects to valves, sensors, and other components. It enables you to program watering schedules and adjust settings based on your specific needs.
Sensors
Sensors provide real-time data to the controller, allowing it to make informed decisions about watering. Common sensors include soil moisture sensors, weather sensors, and rain sensors.
Weather-based system
Some advanced irrigation systems utilize weather data to adjust watering schedules automatically. These systems take into account factors such as rainfall, temperature, and humidity to optimize water usage and prevent over or under watering.
Pumping system
The pumping system is responsible for delivering water from the source to the distribution system. It consists of various components:
Types of pumps
There are different types of pumps used in irrigation systems, including centrifugal pumps, submersible pumps, and turbine pumps. The choice depends on factors such as the water source, required pressure, and flow rate.
Pump capacity
The pump capacity refers to the amount of water the pump can deliver per unit of time. It is essential to select a pump with the appropriate capacity to meet the water demands of the irrigation system.
Pressure requirements
The pressure requirements vary depending on the type of irrigation system and the elevation differences between the water source and the area to be irrigated. The pumping system must be capable of delivering water at the required pressure for efficient distribution.
Distribution system
The distribution system transports water from the pump to the desired irrigation areas. It consists of pipes, fittings, and emitters:
Pipes
Pipes are the backbone of the distribution system, carrying water from the pump to the irrigation zones. The selection of pipe material, diameter, and layout depends on factors such as water pressure, flow rate, and system design.
Fittings
Fittings connect and join different sections of pipes, allowing the distribution system to be flexible and adaptable. Common fittings include couplers, tees, elbows, and valves.
Emitters
Emitters regulate the flow of water and deliver it directly to the plants’ root zones. Drip irrigation systems use emitters such as drippers or micro-sprinklers, while sprinkler systems utilize spray heads or rotor heads.
Irrigation Valves
Irrigation valves control the flow of water within the system. They are essential for dividing the irrigation zones, allowing for independent control of water delivery. Different types of valves serve specific functions:
Types of valves
Common types of irrigation valves include gate valves, ball valves, butterfly valves, and solenoid valves. Each type has its own advantages and applications, such as controlling high flow rates or providing remote control capabilities.
Functioning of valves
Valves can be manually operated or automated using electric or hydraulic systems. They open and close to control the flow of water, allowing precise control over water distribution within the irrigation system.
Backflow Prevention Device
A backflow prevention device is crucial to prevent the contamination of the water supply by backflow, which occurs when water flows in the opposite direction. It is particularly important when using irrigation systems connected to potable water sources:
Why is backflow prevention necessary?
Backflow can introduce pollutants, chemicals, or bacteria into the water supply, posing a health risk. A backflow prevention device prevents this by ensuring that water flows only in the intended direction.
Types of backflow prevention devices
Common backflow prevention devices include atmospheric vacuum breakers, pressure vacuum breakers, and reduced pressure zone assemblies. The appropriate device depends on factors such as the level of protection required and local plumbing codes.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential to keep an irrigation system functioning optimally. Key maintenance tasks include:
- Inspecting and cleaning emitters, sprinkler heads, and filters regularly to remove any obstructions or buildup.
- Checking the distribution system for leaks, damaged pipes, or fittings, and repairing or replacing as needed.
- Calibrating and adjusting the controller to ensure accurate watering schedules.
- Monitoring and adjusting water pressure to avoid over or under watering.
- Winterizing the system to protect it from freezing temperatures.
Common issues and troubleshooting tips
Despite proper maintenance, irrigation systems may encounter occasional issues. Here are some common problems and troubleshooting tips:
- Low water pressure: Check for obstructions in the distribution system, such as clogged filters or partially closed valves. Ensure the pump is operating correctly and that there are no leaks in the system.
- Uneven water distribution: Inspect and clean emitters or sprinkler heads that may be clogged or damaged. Adjust the spray patterns and ensure proper spacing for uniform coverage.
- Electrical malfunctions: Check the controller and electrical connections for any issues. Verify that power is reaching the pump and valves. Consider consulting a professional if the problem persists.
- Water wastage or excessive runoff: Verify that the watering schedule and duration are appropriate for the plants’ needs. Adjust the emitter flow rates or sprinkler heads to prevent overspray and minimize water waste.
By understanding the different components of an irrigation system, selecting the appropriate water source, and ensuring regular maintenance, you can effectively manage water resources and promote healthy plant growth. Whether you are a farmer, gardener, or landscape enthusiast, an irrigation system will greatly enhance your ability to sustainably and efficiently water your plants.

This post may contain affiliate links which means I may receive a commission for purchases made through links. Learn more on my Private Policy page.
