This post may contain affiliate links which means I may receive a commission for purchases made through links. Learn more on my Private Policy page.
If you’re looking to streamline your farming practices and increase productivity, implementing automation might be the solution you’ve been searching for. By integrating advanced technologies and systems into your farm, you can automate various tasks and processes, resulting in improved efficiency and reduced labor costs. From robotic harvesting and planting to automated irrigation and monitoring systems, this article will provide you with valuable insights on how to incorporate automation into your farming practices and take your agricultural business to the next level.

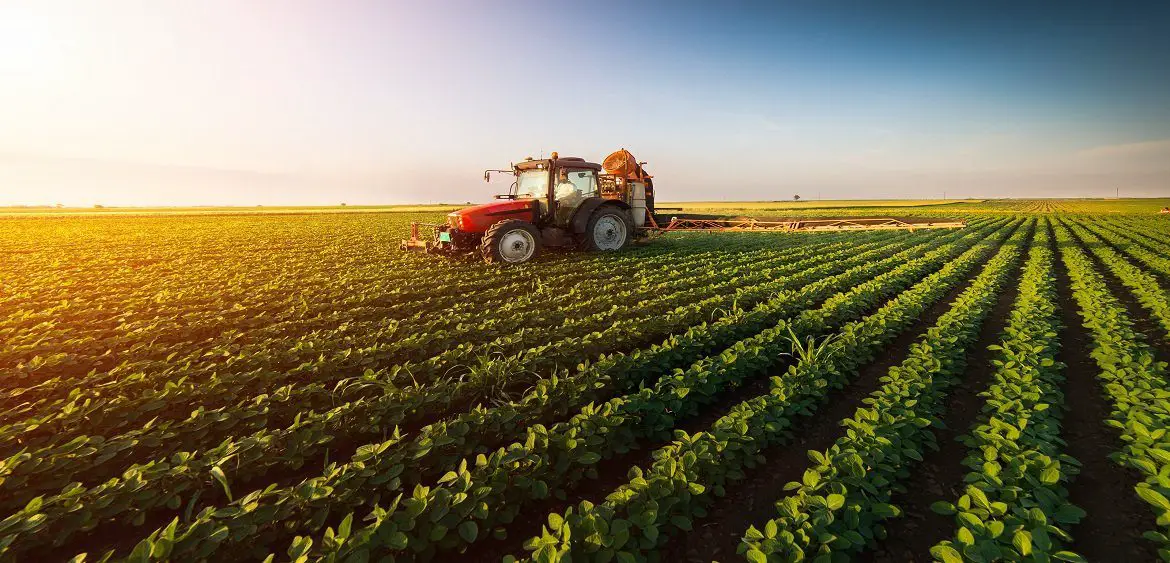
This image is property of civileats.com.
Introduction to Automation in Farming
Understanding the concept of automation
Automation in farming refers to the use of technology and machinery to perform various tasks and processes in agricultural practices. This includes replacing manual labor with machines and integrating computer systems to streamline and optimize farm operations. The goal is to increase efficiency, productivity, and profitability while reducing the reliance on human labor.
Benefits of automation in farming
The adoption of automation in farming offers a wide range of benefits. Firstly, it reduces the workload on farmers and laborers by automating repetitive and labor-intensive tasks. This frees up their time and allows them to focus on more important aspects of farm management. Secondly, automation enhances accuracy and precision, resulting in improved crop yield and quality. By utilizing technology such as precision planting and seeding, farmers can ensure optimal plant spacing and placement, leading to better yields. Furthermore, automation can help farmers make data-driven decisions by collecting and analyzing farm data, allowing for better resource allocation and optimized farm operations. Lastly, automation can significantly reduce production costs in the long run, making farming more financially sustainable.
Identifying Automation Opportunities in Farming
Assessing current farming practices
To identify the potential areas for automation, it is crucial to first assess the current farming practices. This involves evaluating the tasks and processes involved in crop production or livestock management and identifying areas that can be made more efficient through automation.
Identifying repetitive tasks
Repetitive tasks are excellent candidates for automation as they often require little decision-making and are easily adaptable to machines or computer systems. Tasks such as seeding, transplanting, weeding, and harvesting can be automated, reducing the need for manual labor.
Analyzing labor-intensive processes
Labor-intensive processes, which consume significant time and effort, can also be automated to save resources and increase efficiency. Examples include irrigation management, fertilization, and pest control, which can be optimized through the use of automated systems.
Considering climate and environmental factors
Automation technologies should also be selected based on the specific climate and environmental factors of the farm. For instance, farms located in arid regions may benefit from automated irrigation systems to conserve water, while farms in colder climates might require technologies that can withstand extreme temperatures.
Exploring available automation technologies
Farmers should explore the various automation technologies available in the market. These include robotic systems, automated feeding systems, remote monitoring devices, and precision agriculture tools. Understanding the features, capabilities, and costs of these technologies is essential for making informed decisions.
Choosing the Right Automation Technology
Understanding different types of automation technologies
There are different types of automation technologies available for farming purposes, and it is essential to understand their functionalities and suitability. Robotic systems, unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), sensor technologies, and computer systems are some examples of automation technologies that can be employed in farming practices.
Evaluating cost and ROI
When choosing automation technology, cost and return on investment (ROI) should be carefully considered. Assessing the initial investment required, including purchasing and installation costs, and comparing it with the long-term benefits and potential cost savings can help determine if the technology is financially viable for the farm.
Analyzing suitability for specific farming practices
Each farming practice has its unique requirements, and automation technologies should be evaluated for their compatibility and suitability. For example, robotic harvesting and sorting may be suitable for large-scale crop production, while precision planting technologies may be more beneficial for small-scale farms.
Considering scalability and future needs
Automation technologies should be scalable and adaptable to future needs. It is important to consider both the current requirements and possible expansions or changes in farming practices. This ensures that the chosen technology can accommodate the farm’s growth and evolving needs over time.
Implementing Automation in Crop Production
Automating irrigation systems
Automated irrigation systems help farmers efficiently manage water usage by delivering the right amount of water at the right time. These systems can be programmed to monitor soil moisture levels and adjust irrigation accordingly, ensuring optimal crop growth while conserving water resources.
Using precision planting and seeding
Precision planting and seeding technologies enable farmers to optimize plant spacing and placement, resulting in improved crop yield and uniformity. These technologies use GPS and computer-controlled equipment to precisely measure and place seeds or seedlings, reducing waste and maximizing plant growth.
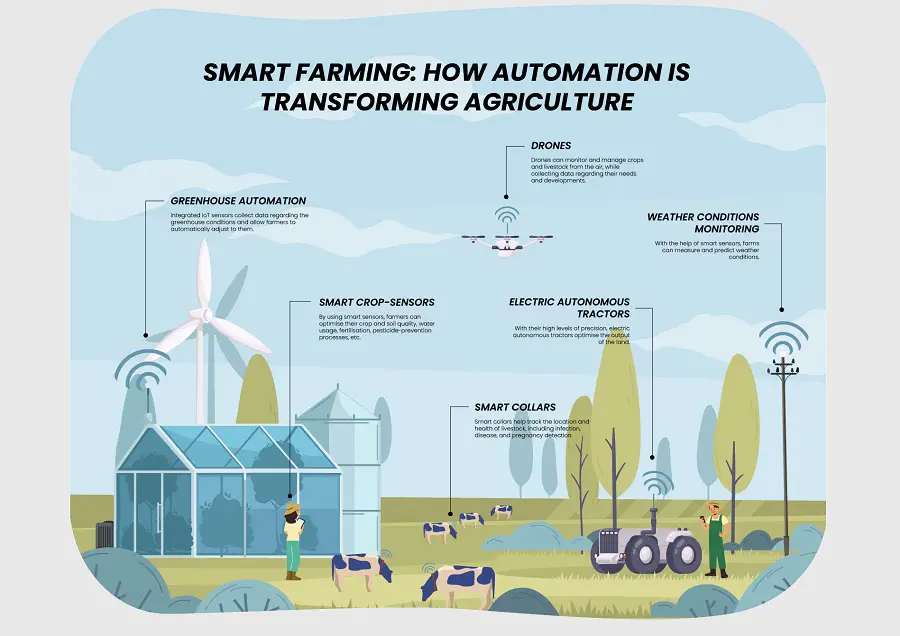
Deploying automatic monitoring and data collection
Automatic monitoring systems, such as sensors and drones, allow farmers to collect real-time data on crop health, soil conditions, and weather patterns. This data can be used to make informed decisions, such as adjusting irrigation and applying fertilizers or pesticides, leading to better crop management.
Implementing automated crop nutrient management
Automated crop nutrient management systems help farmers optimize fertilizer use based on crop needs and soil conditions. These systems can monitor nutrient levels and automatically adjust fertilizer application, reducing waste and minimizing the risk of over or under-fertilizing.
Utilizing robotic harvesting and sorting
Robotic harvesting and sorting systems are particularly beneficial for labor-intensive crops. These robots are equipped with advanced sensors and mechanisms to identify ripe produce, harvest them, and sort them based on quality, size, or other criteria. This automation reduces the reliance on manual labor, improves efficiency, and ensures consistent produce quality.
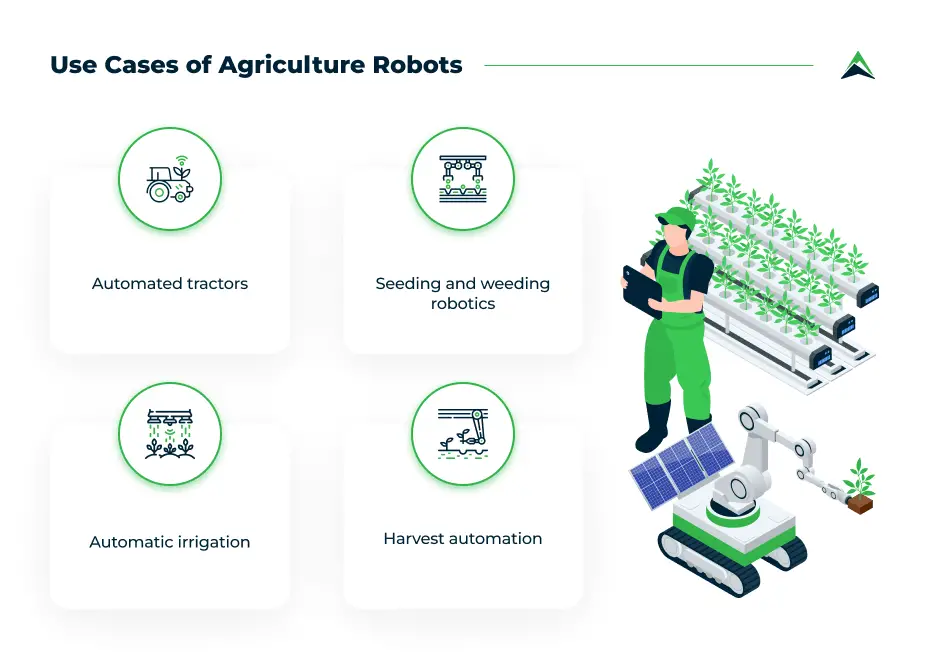
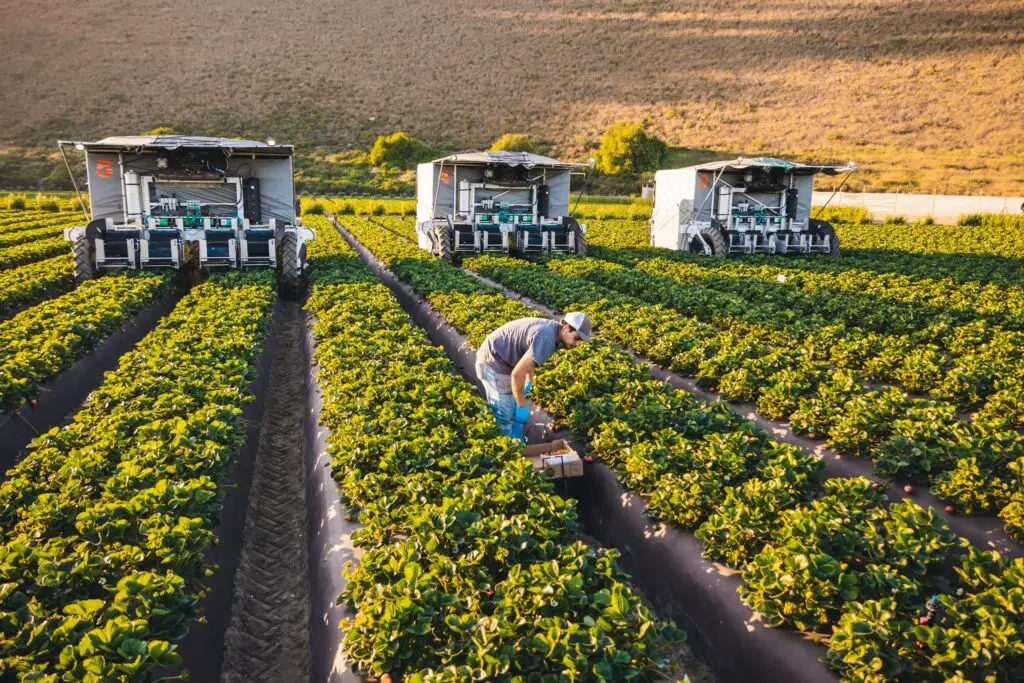
This image is property of s8.easternpeak.com.
Automation in Livestock Management
Automated feeding systems
Automated feeding systems eliminate the need for manual feeding of livestock. These systems use sensors and computer-controlled mechanisms to dispense feed in predetermined quantities and schedules. This ensures that the animals receive optimal nutrition while relieving the farmers of the daily feeding responsibilities.
Remote monitoring of animal health and behavior
Remote monitoring devices, such as wearable sensors or cameras, allow farmers to monitor the health and behavior of their livestock from a distance. This enables early detection of illnesses or distress, allowing for timely intervention and improved animal welfare.
Robotic milking and shearing
Robotic milking and shearing systems streamline the milking and shearing processes in dairy and wool production. These machines use sensors and computer algorithms to perform these tasks automatically, reducing the labor requirements and enhancing efficiency.
Automated waste management solutions
Automated waste management solutions, such as manure collection and processing systems, help farmers manage and utilize animal waste effectively. These systems can collect, treat, and repurpose manure, reducing environmental pollution and providing a valuable source of organic fertilizers and energy.
Integrating Data Analytics and AI in Farming Automation
Collecting and analyzing farm data
Farmers can collect data from various sources, such as sensors, drones, and weather stations, to gather valuable information about soil conditions, crop health, and environmental factors. Analyzing this data provides insights for decision-making and optimizing farm operations.
Implementing AI-driven decision-making
Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies can be utilized to analyze and interpret farm data, allowing for more accurate and timely decision-making. AI algorithms can assess soil and weather data, identify disease patterns in crops or livestock, and recommend appropriate actions or treatments, leading to improved farm management.
Utilizing predictive analytics for optimized farm operations
Predictive analytics uses historical data and AI algorithms to forecast future outcomes and trends. By implementing predictive analytics in farm automation, farmers can anticipate weather patterns, predict crop yields, and optimize resource allocation, enabling more efficient and productive farming practices.

This image is property of www.progressiveautomations.com.
Overcoming Challenges in Farm Automation Implementation
Initial investment and financial considerations
One significant challenge in implementing farm automation is the initial investment required. The cost of purchasing and installing automation technologies can be a deterrent for some farmers. However, thorough cost-benefit analysis, assessing long-term savings and overall farm efficiency, can help justify the investment.
Technological compatibility and integration
Integrating automation technologies with existing farm systems and equipment can be complex. Ensuring compatibility between different technologies and optimizing their integration requires technical expertise and careful planning. Farmers should seek assistance from experts or technology providers to ensure a seamless integration process.
Training and reskilling farm workers
Implementing automation may require farmers and farm workers to acquire new skills and knowledge. Training programs should be provided to equip them with the necessary competencies to operate and maintain the automation technologies effectively. Reskilling programs can help ensure that workers can adapt to changing roles and responsibilities in an automated farming environment.
Addressing potential job displacement concerns
The implementation of automation in farming may raise concerns about job displacement. However, it is important to emphasize that automation can create new employment opportunities in the form of technology maintenance and management, data analysis, and skilled operation of automated systems. Communicating this potential and providing support for affected workers can help alleviate concerns.
Dealing with technical failures and maintenance
Like any technology, automation systems may encounter technical failures or require regular maintenance. Planning for regular check-ups, system updates, and having contingency plans in place is crucial to ensure minimal disruption to farm operations. Additionally, establishing relationships with technology providers or local service centers can expedite troubleshooting and maintenance processes.
Ensuring Cybersecurity in Farm Automation
Understanding potential cybersecurity risks
As automation involves the use of computer systems and networks, it is essential to address potential cybersecurity risks. Threats such as data breaches, unauthorized access, and malware attacks can compromise farm operations and sensitive information. Understanding these risks is the first step in implementing effective cybersecurity measures.
Implementing robust data encryption
To protect sensitive farm data, encryption should be implemented. Encryption algorithms ensure that data transmitted or stored is converted into unreadable formats, making them difficult for unauthorized individuals to access.
Securing network infrastructure
Farm networks and communication systems should be secured to prevent unauthorized access and potential cyber intrusions. This involves using firewalls, regularly updating security protocols, and implementing strong user authentication processes.
Regularly updating software and firmware
Keeping automation technologies’ software and firmware up to date is crucial for maintaining security. Manufacturers often release updates to address vulnerabilities and enhance system performance. Regularly reviewing and implementing these updates helps protect against potential cybersecurity threats.
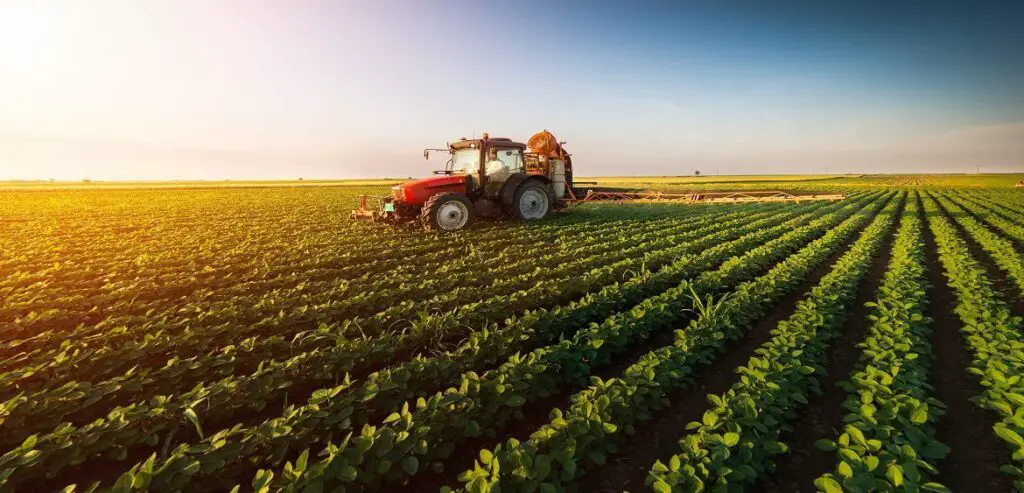
This image is property of itsupplychain.com.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of Farm Automation
Farm A: Automating dairy operations
Farm A, a large-scale dairy farm, implemented automation technologies such as robotic milking systems and automated feeding systems. This reduced labor requirements and improved milk production efficiency. Additionally, remote monitoring devices were used to track the health and behavior of the cows, ensuring timely intervention when necessary.
Farm B: Precision agriculture and IoT integration
Farm B, a medium-sized crop farm, integrated precision planting technology with Internet of Things (IoT) devices. This allowed for real-time monitoring of soil moisture levels, temperature, and weather conditions. By using AI-driven decision-making, they optimized irrigation schedules and resource allocation, resulting in increased crop yield and water efficiency.
Farm C: Robotic solutions for vineyard management
Farm C, a vineyard, adopted robotic solutions for vineyard management. Automated sensors and robots were used to monitor grape ripeness and automate harvesting processes. This increased efficiency, reduced labor costs, and improved the quality and consistency of the harvested grapes.
Conclusion
Automation in farming offers numerous benefits, from increased efficiency and productivity to reduced labor requirements and cost savings. By assessing farming practices, identifying automation opportunities, and choosing the right technologies, farmers can streamline their operations and optimize crop production or livestock management. Integrating data analytics and AI further enhances decision-making and enables predictive analytics for improved farm operations. Overcoming challenges such as initial investment, training, and cybersecurity risks is crucial for successful implementation. By learning from successful case studies, farmers can gain insights on how automation has revolutionized farming practices. Embracing automation can pave the way for a more sustainable and profitable future in agriculture.

This image is property of pnptc-media.s3.amazonaws.com.
This post may contain affiliate links which means I may receive a commission for purchases made through links. Learn more on my Private Policy page.

