This post may contain affiliate links which means I may receive a commission for purchases made through links. Learn more on my Private Policy page.
Imagine a world where seeds have the power to withstand harsh environmental conditions and successfully generate healthy crops. It may sound like something out of a science fiction novel, but seed coatings have made this dream a reality. By providing a protective shield against various environmental stresses, such as drought, disease, and extreme temperatures, seed coatings play a crucial role in ensuring the survival and productivity of plants. In this article, we will explore the fascinating world of seed coatings and the ways they contribute to the resilience and sustainability of our agricultural practices. So, get ready to uncover the hidden secrets behind these unassuming yet remarkable guardians of our food security.
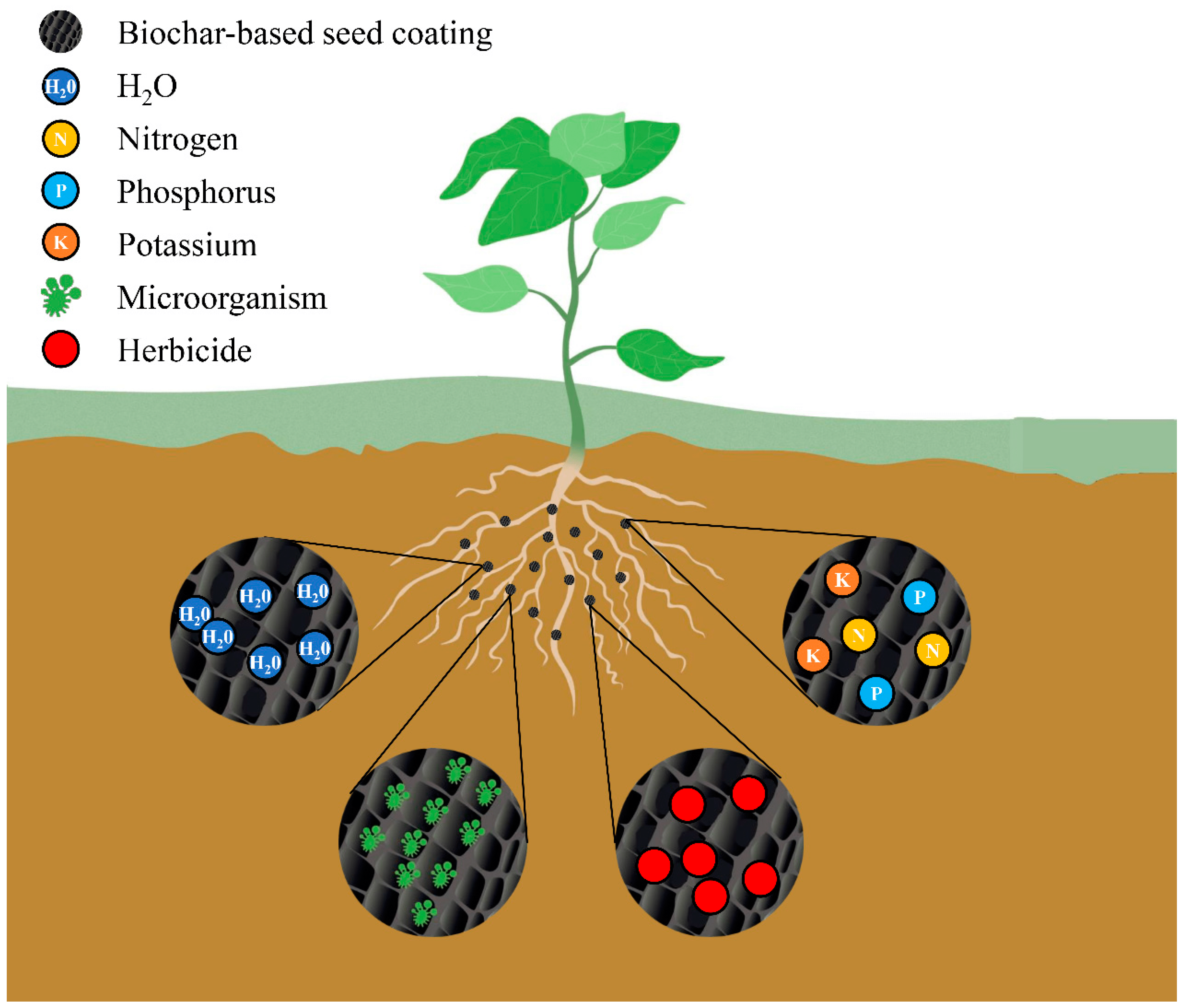
Introduction to Seed Coatings
Seed coatings play a vital role in modern agriculture by providing a protective layer around seeds, enhancing their performance, and promoting sustainability. These coatings serve as a barrier against environmental stresses, protect against disease, and optimize nutrient uptake for better crop yield and quality. Understanding the types of seed coatings, their benefits, and techniques for application is essential for the successful implementation of seed coating technology in agriculture.
Definition of Seed Coatings
Seed coatings refer to a thin layer of material applied to the surface of seeds. This layer can be made from various substances, such as polymers, clay, minerals, or specialized formulations. The coating adheres to the seed surface, forming a protective shield that improves seed performance and protects against environmental stresses.
Importance of Seed Coatings in Agriculture
Seed coatings have become increasingly important in modern agriculture due to their numerous benefits. By providing a protective layer, seed coatings help seeds withstand adverse conditions such as extreme temperatures, moisture stress, and disease attacks. They also enhance seed performance, improve nutrient uptake, reduce pesticide use, and contribute to environmental sustainability. Seed coatings have revolutionized the way crops are grown, leading to increased crop yield, enhanced quality, and preservation of genetic diversity.
Types of Seed Coatings
-
Film coatings: Film coatings consist of a thin, transparent layer applied to the seed surface. These coatings often contain fungicides, insecticides, or growth-promoting substances. Film coatings provide protection against external factors, such as UV radiation, while allowing gas exchange between the seed and its surroundings.
-
Encrustment coatings: Encrustment coatings involve applying a thick layer of material to the seed surface, forming a rough and irregular external layer. This type of coating offers physical protection and helps retain moisture around the seed, promoting germination and seedling establishment.
-
Pelleting coatings: Pelleting coatings involve mixing seeds with a carrier material, such as clay or vermiculite, to form larger, rounded particles. The coating helps with seed handling, allowing easier and more precise planting. It also serves as a protective layer while providing a better seed-to-soil contact for improved germination rates.
-
Encapsulation coatings: Encapsulation coatings consist of coating seeds with a biopolymer or polysaccharides, forming small capsules. These coatings protect against external stresses and deliver nutrients or bioactive substances directly to the seed. Encapsulation coatings are particularly useful in seed treatment to prevent specific diseases or enhance nutrient availability.

Seed Coatings as a Protective Layer
Seed coatings act as a protective layer, shielding the seeds from various environmental stresses. Here are some key ways in which seed coatings provide protection:
-
Barrier against environmental stresses: Seed coatings create a physical barrier between the seed and its surroundings, protecting it from harmful factors such as extreme temperatures, UV radiation, and drying. This barrier minimizes seed damage and maintains seed viability, ensuring successful germination and seedling establishment.
-
Protection against extreme temperatures: Extreme temperatures can negatively impact seed vitality and germination rates. Seed coatings provide insulation, reducing heat stress or cold injury caused by fluctuating temperatures. This protection helps seeds maintain their integrity and physiological processes, resulting in better overall crop performance.
-
Protection against moisture stress: Moisture stress can hinder germination and seedling establishment. Seed coatings help retain moisture and create a microenvironment conducive to germination and seedling growth. By preventing excessive desiccation or saturation, seed coatings ensure optimal water availability for the seeds, promoting successful germination even in challenging conditions.
Seed Coatings and Disease Resistance
Seed coatings play a crucial role in protecting seeds against diseases caused by seed-borne and soil-borne pathogens. Here’s how seed coatings contribute to disease resistance:
-
Prevention of seed-borne diseases: Seed coatings can be formulated with fungicides or biocontrol agents to prevent seed-borne diseases. These coatings create a chemical barrier that inhibits the growth and establishment of pathogens on the seed surface, reducing the risk of disease transmission during planting.
-
Protection against soil-borne pathogens: Seed coatings can also incorporate biopesticides or antifungal agents to protect against soil-borne pathogens. When seeds are coated with these substances, they act as a barrier against pathogens present in the soil, preventing infection and subsequent crop damage.

Seed Coating Techniques
There are various techniques for applying seed coatings, ranging from conventional methods to advanced technologies. These techniques ensure optimal coverage and adhesion of the coating material to the seed surface. Here are two common seed coating techniques:
-
Conventional seed coating methods: Conventional seed coating methods involve manually or mechanically applying coating materials to seeds. This can be done by mixing seeds with the coating material in a rotating drum, applying the coating using an air gun, or immersing seeds in a solution of the coating material. Conventional methods are relatively simple and cost-effective, making them suitable for small-scale operations.
-
Advanced seed coating techniques: Advanced seed coating techniques often employ specialized equipment, such as fluidized bed coaters or electrostatic seed coaters. These techniques ensure precise and uniform coating application, resulting in better seed performance. Advanced techniques also allow for the incorporation of multiple active ingredients in the coatings, providing enhanced protection against diseases and environmental stresses.
Enhancing Seed Performance with Coatings
Seed coatings significantly improve seed performance, leading to better germination rates, enhanced seed vigour, and increased seedling establishment. Here’s how seed coatings contribute to enhanced seed performance:
-
Improved seed germination: Seed coatings can enhance germination rates by providing a favorable microenvironment for seed imbibition and germination. The coatings retain moisture around the seed, promote gas exchange, and protect against external factors, leading to faster and more uniform germination.
-
Enhanced seed vigour: Seed coatings enhance seed vigour by protecting against stresses that can weaken or damage seeds. The coatings provide insulation against extreme temperatures and act as a physical barrier against external threats, allowing seeds to maintain their vigor and physiological integrity.
-
Increased seedling establishment: Coated seeds often exhibit better seedling establishment due to improved germination rates and seed vigor. The coatings protect the seeds during the critical early stages of growth, ensuring optimal conditions for seedling emergence and establishment. This leads to more uniform stands and higher crop productivity.

Seed Coatings and Nutrient Uptake
Seed coatings can optimize nutrient uptake by seeds and seedlings, promoting better crop growth and development. Here’s how seed coatings enhance nutrient availability:
-
Slow-release fertilizers in seed coatings: Seed coatings can incorporate slow-release fertilizers, such as controlled-release nitrogen or phosphorus sources. These fertilizers are released gradually over time, providing a continuous supply of nutrients to the developing seedlings. Slow-release fertilizers in seed coatings ensure efficient nutrient utilization and reduce nutrient losses, leading to healthier and more productive crops.
-
Enhanced nutrient availability to the seedlings: Seed coatings can improve the availability of essential nutrients to seedlings by incorporating micronutrients or other plant growth-promoting substances. The coatings ensure that these nutrients are in close proximity to the developing roots, facilitating their uptake and utilization by the seedlings. This targeted delivery of nutrients promotes early plant growth, development, and overall crop productivity.
Role of Seed Coatings in Environmental Sustainability
Seed coatings contribute to environmental sustainability in various ways, promoting resource efficiency and reducing the environmental impact of agricultural practices. Here are some key roles of seed coatings in environmental sustainability:
-
Reduced pesticide use: Seed coatings containing fungicides, insecticides, or biocontrol agents can reduce the need for foliar applications of pesticides. By protecting seeds from diseases and pests, the coatings minimize the reliance on external pesticide inputs, resulting in reduced environmental contamination and overall pesticide use.
-
Improved crop yield and quality: Seed coatings promote crop yield and quality by providing optimal conditions for germination, seedling establishment, and nutrient uptake. By ensuring successful early growth stages and adequate nutrient availability, seed coatings contribute to higher crop productivity. This leads to better resource utilization and reduced pressure on land, water, and other agricultural inputs.
-
Preservation of genetic diversity: Seed coatings can help preserve genetic diversity by protecting seeds of rare or endangered plant species. By safeguarding the viability and germination capacity of these seeds, coatings play a crucial role in conservation efforts. This ensures the availability of diverse genetic resources for future crop improvement and ecosystem restoration initiatives.

Challenges and Future Directions
While seed coatings offer significant benefits, there are still challenges and opportunities for improvement in this field. Here are some challenges and future directions for seed coatings:
-
Development of eco-friendly coatings: Developing environmentally friendly coatings that are biodegradable and free from toxic substances is a major challenge. Research and development efforts should focus on exploring sustainable materials and formulations that meet both performance and ecological criteria.
-
Tailoring coatings for specific crops and environments: Different crops and environmental conditions require specific seed coating formulations and techniques. Customizing coatings to suit the needs of individual crops, soils, and climates will maximize their effectiveness and address specific challenges faced by farmers in different regions.
-
Improving coating application techniques: Enhancements in coating application techniques can improve the efficiency and reliability of seed coatings. Advancements in equipment design, application methods, and coating formulations can result in more precise and uniform coating coverage, leading to better seed performance.
Conclusion
Seed coatings play a crucial role in modern agriculture by providing a protective layer around seeds, enhancing their performance, and promoting environmental sustainability. They act as a barrier against environmental stresses, protect against diseases, optimize nutrient uptake, and reduce pesticide use. Understanding the different types of seed coatings, their benefits, and application techniques is essential for maximizing crop productivity and ensuring sustainable agricultural practices. By harnessing the power of seed coatings, farmers can cultivate resilient, high-yielding crops and contribute to a more sustainable future for our planet.
This post may contain affiliate links which means I may receive a commission for purchases made through links. Learn more on my Private Policy page.
