This post may contain affiliate links which means I may receive a commission for purchases made through links. Learn more on my Private Policy page.
If you’re interested in gaining a deeper understanding of the most popular irrigation systems used in modern farming, look no further! This article will provide you with a comprehensive overview of the innovative techniques that farmers across the globe employ to efficiently water their crops. From the advancements in drip irrigation that save water and reduce wastage to the convenience of center pivot irrigation systems, we’ll explore the practicality and effectiveness of each method. So, grab a cup of tea and get ready to discover the irrigation systems that have revolutionized modern agriculture.
1. Drip Irrigation
Overview of Drip Irrigation
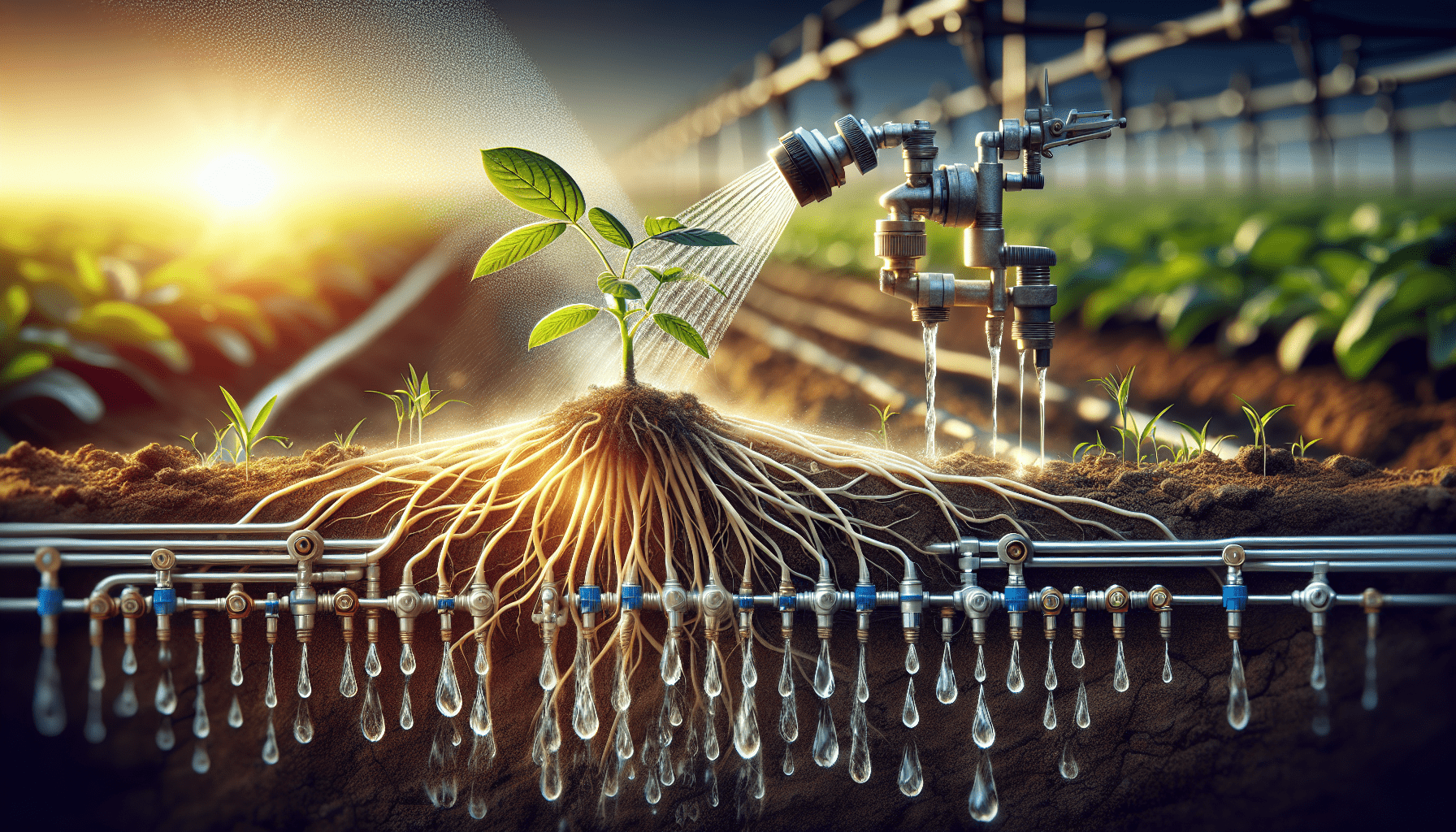
Drip irrigation is a highly efficient and precise method of watering plants and crops. It involves delivering small, controlled amounts of water directly to the root zone of plants, minimizing water waste and optimizing plant growth. In this irrigation method, water is distributed through a network of tubes, pipes, and emitters that deliver water at a slow and steady pace.
Advantages of Drip Irrigation
There are several advantages of using drip irrigation in farming. Firstly, it helps conserve water as it delivers water directly to the roots, reducing evaporation and runoff. Drip irrigation also allows for precise control over the amount of water delivered, ensuring that each plant receives the appropriate amount for its needs. This not only promotes healthy plant growth but also reduces the risk of overwatering or underwatering.
Secondly, drip irrigation is highly efficient in terms of labor and time. Once the system is properly set up, it requires minimal maintenance and can be automated, saving farmers valuable time and resources. Additionally, drip irrigation reduces weed growth by delivering water only to the intended plants, minimizing weed competition and reducing the need for herbicides.
Lastly, drip irrigation is environmentally friendly. By reducing water usage and preventing runoff, it helps conserve water resources and protect the surrounding ecosystem. It also reduces the risk of soil erosion and nutrient leaching, preserving the quality of the soil.
Disadvantages of Drip Irrigation
Although drip irrigation offers numerous benefits, there are a few disadvantages to consider. One of the primary concerns is the initial cost of installation. Setting up a drip irrigation system can be expensive, especially for large farming operations. However, it is important to consider the long-term savings in water and labor costs that outweigh the initial investment.
Another disadvantage is the potential for clogging of the emitters or tubes. This can occur due to the presence of sediment, minerals, or organic matter in the water supply. Regular maintenance, such as filtration and flushing of the system, is necessary to prevent clogs and ensure proper functioning.
Lastly, drip irrigation may not be suitable for certain soil types. Heavy clay soils, for example, may have poor water infiltration rates, leading to puddling or water saturation issues. Soil assessment and proper system design are crucial to overcome these challenges and ensure optimal irrigation efficiency.
Components of Drip Irrigation System
A drip irrigation system consists of various components that work together to deliver water to the plants. These include:
- Water source: This can be a well, pond, or municipal water supply.
- Pump or pressure regulator: Used to provide the necessary pressure for water flow in the system.
- Mainline: A large-diameter pipe that transports water from the source to the field.
- Submain: Smaller diameter pipes that distribute water from the mainline to individual rows or sections of crops.
- Emitters: Devices that deliver water directly to the plants. They can be inline emitters, which are integrated into the tubing, or individual emitters inserted into the tubing.
- Filters: Used to remove sediment, debris, and particles that could clog the emitters.
- Backflow preventers: Ensure that water does not flow back into the water source, preventing contamination.
- Pressure regulators: Maintain a consistent pressure throughout the system to ensure proper water delivery.
- Timer or controller: Enables automation of the irrigation schedule.
- Optional features: These include sensors for moisture, temperature, or humidity, which can enhance irrigation efficiency and plant health.
Types of Drip Irrigation Systems
There are three main types of drip irrigation systems:
-
Point-Source Drip System: This system uses individual emitters placed near each plant. It is suitable for small-scale applications or gardens with different water requirements for each plant.
-
Inline Drip System: In this system, emitters are integrated into the tubing, evenly distributing water along the entire length. It is commonly used in row crops or large-scale agricultural operations.
-
Subsurface Drip System: As the name suggests, this system places the irrigation tubing below the soil surface, delivering water directly to the roots. It is particularly useful in arid regions with high evaporation rates.
Drip Irrigation Maintenance
Proper maintenance is essential to keep a drip irrigation system in optimal condition. Regular tasks include:
- Flushing the system to remove any clogs or sediments that may accumulate over time.
- Checking and replacing worn-out emitters or tubing.
- Monitoring the system for leaks or damaged components.
- Adjusting the system as plant growth progresses to ensure proper water distribution.
- Inspecting and cleaning filters to prevent clogs.
By following these maintenance practices, farmers can ensure the longevity and efficiency of their drip irrigation system, resulting in healthier plants and increased crop yields.
This post may contain affiliate links which means I may receive a commission for purchases made through links. Learn more on my Private Policy page.